Part 1: Preventing Hand Injuries
One of the key ways to work safer is to prevent hand injuries. Incidents of this type often occur during equipment maintenance, assembly line work – and especially during bolting, where pinch points are a common hazard.
Ways to avoid hand injuries include:
- Wearing proper safety gloves to suit the job
- If you are the tool operator, let your co-worker know your hands are in a safe position
- Choosing tools with features that reduce the risk of hand injuries, such as those described below.

Ergonomic Hydraulic Torque Wrenches
When investing in a hydraulic torque wrench, make sure you specify ergonomic safety handles. A tool with a correctly positioned handle will help to minimize the risk of hand injuries or strains. Examples include the Enerpac S, W, HMT, and DSX-Series.
Backup Spanners
Adding to the safety of bolting applications, the BUS-Series Back-Up Spanners are hands-free tools that improve safety. They are lightweight, spark-free, and non-impact. Each spanner includes a safety cable with a quick-connect carabiner, stainless steel tethers, and secure Allen-key fixings.
Flange Spreading Wedges
Enerpac SWi-Series spreaders are engineered to overcome finger pinch points. These have increased step-depth on upper steps and forged main components for high strength and reliability. Handles are ergonomically positioned over the center of the spreader and revolve to aid horizontal or vertical spreading. Also provided as standard are safety blocks and lanyards 1.0 m (39″) in length.
Portable Machining Tools
Machining tools used onsite typically use rotating parts and therefore present a trapping hazard. There’s also the potential of injury from the swarf or metal chippings flying out into the surrounding area.
Standing well clear of the machine and wearing PPE will help, as will using a remote pendant wherever possible. Enerpac pneumatic on-site machining tools are equipped with a two-hand deadman handle that prevents accidental start-up of equipment. They require the operator to have both hands on the valve – ensuring that hands are a safe distance away from moving parts at start-up.
Part 2: Work Safer in Explosive Atmospheres

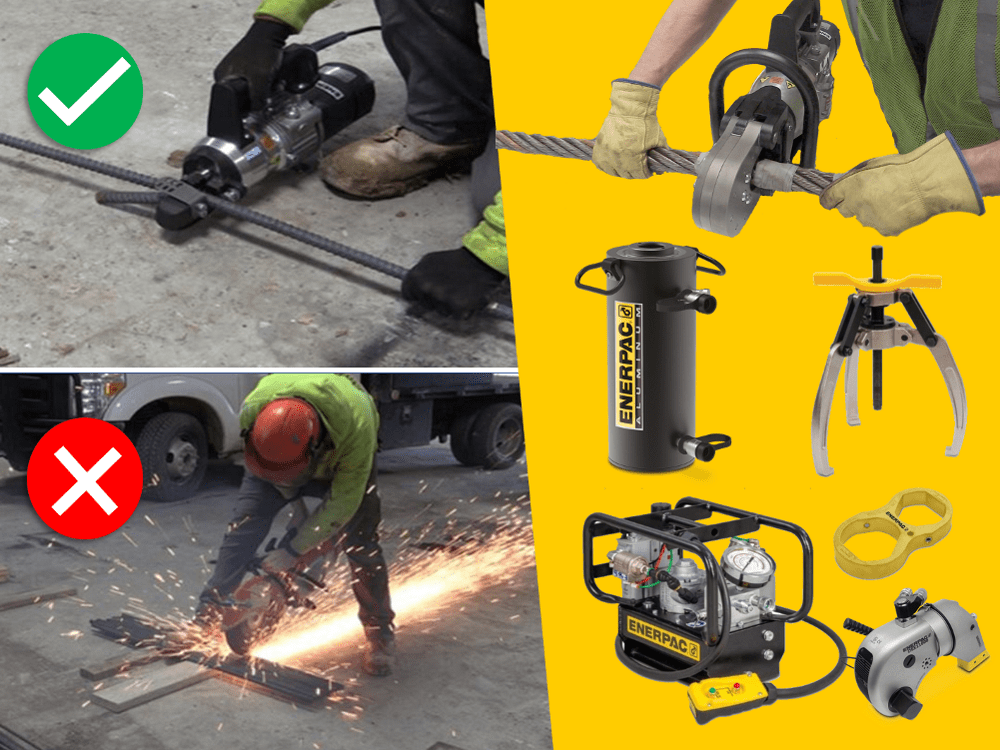
Above left: spark-free cutting of metal bar. Right: Using an angle grinder.
Any hot working process has the potential to trigger a fire – especially if carried out near flammable substances. Serious or fatal injuries can occur if control measures are not in place.
Before carrying out any hot work, keep a lookout for the following:
- Identify combustible materials in the area, including rubbish, paper, or dust
- Ensure the area is well-ventilated
- Consider safer mechanical or hydraulic tools to reduce the risk of spark or flame
Spark Free Cutting with Hydraulic and Mechanical Cutters

Whenever you need to cut bar, chain, cable, nuts, or other materials, Enerpac hydraulic and mechanic cutters will help you do this with minimal risk of sparks. This is safer than methods such as torching, grinding, and sawing, which expose users to the risks of exploding blades, sparks, and open flames. The controlled cutting process with the Enerpac cutters also prevents Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAV).
See the video below which compares a hydraulic bar cutter with a gas saw.
The video below compares a hydraulic chain cutter with an angle grinder.